The centrality of Digital Literacy to Citizen Interaction with E-government Services in Tanzania
A Literature Review
- 2025-10-06 (2)
- 2024-06-18 (1)
Versions
- 2025-10-06 (2)
- 2024-06-18 (1)
Downloads
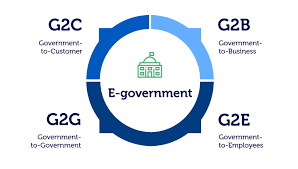
The quest for promoting digital literacy among the populace to access e-government services is more critical than ever because the implementation and success of e-governance depend on digital literacy. This paper envisions a successful change towards the realisation of using electronic government services as a directed development dependent upon the presence of specific empowering agents, such as building digital literacy among the populace. The paper employs a literature review of various sources to understand better the emerging situation of digitalising government services and the determinants of digital technologies used to access egovernment service provision. Findings indicate that top-down-oriented initiatives are studied mainly on how they lead to the successful implementation of e-government rather than how the bottom-up approaches have been successfully applied to yield the expected results of egovernment service provision. The work is expected to provide practitioners of digitalisation of government services with theoretical and policy gaps that must be addressed when dealing with e-government service delivery to citizens with mostly inadequate digital literacy. Topical gaps in the literature are identified as areas for future research. The study is based on findings from the literature review, specifically on the role of digital literacy in the use of e-government services in Tanzania. More studies are needed to include findings from Africa and elsewhere to get a clearer global perspective about the need for digital literacy for the successful implementation of servitisation of government services.